Top Textile Machinery Types You Need to Know About?
The textile machinery industry plays a crucial role in global manufacturing. The sector is projected to grow significantly, reaching approximately $267 billion by 2024. This growth reflects increasing demand for efficient and innovative textile production processes. Understanding the various types of textile machinery is essential for manufacturers aiming to remain competitive.
Different types of textile machinery, such as weaving looms, knitting machines, and dyeing equipment, serve specific functions. Each category has unique features that enhance productivity and quality. However, many manufacturers struggle to choose the right machinery for their needs. This can lead to inefficient production and increased costs.
With the continuous evolution of technology, staying updated on the latest textile machinery is vital. Failure to invest in modern equipment could hinder a company’s growth. An informed approach to machinery selection can optimize production and improve overall efficiency. The textile machinery landscape is complex, and understanding its nuances is key for success.

Overview of Textile Machinery: Importance and Applications
The textile machinery sector plays a vital role in the global economy. This industry is expected to reach a valuation of $120 billion by 2025, according to recent market analysis. Textile machinery includes various types, from spinning machines to weaving and knitting machines. Each type serves a unique purpose in the production process.
Understanding this machinery's importance can enhance productivity. Spinning machines reduce fiber processing time, while weaving machines improve fabric consistency. This ultimately leads to cost savings. However, many manufacturers struggle to keep up with technology. They often rely on outdated equipment, which hampers efficiency and quality. Regular maintenance and tech upgrades are essential for staying competitive.
**Tips**: Invest in training your staff. Knowledgeable employees can maximize machinery potential. Upgrading machinery might seem costly, but it can significantly enhance output. Consider local suppliers to reduce downtime. Identifying machinery gaps can lead to substantial long-term savings.
Top Textile Machinery Types You Need to Know About
This chart illustrates the number of textile machinery units sold across various types, providing insight into the popularity and market demand of these machines in the textile industry.
Key Types of Spinning Machinery in the Textile Industry
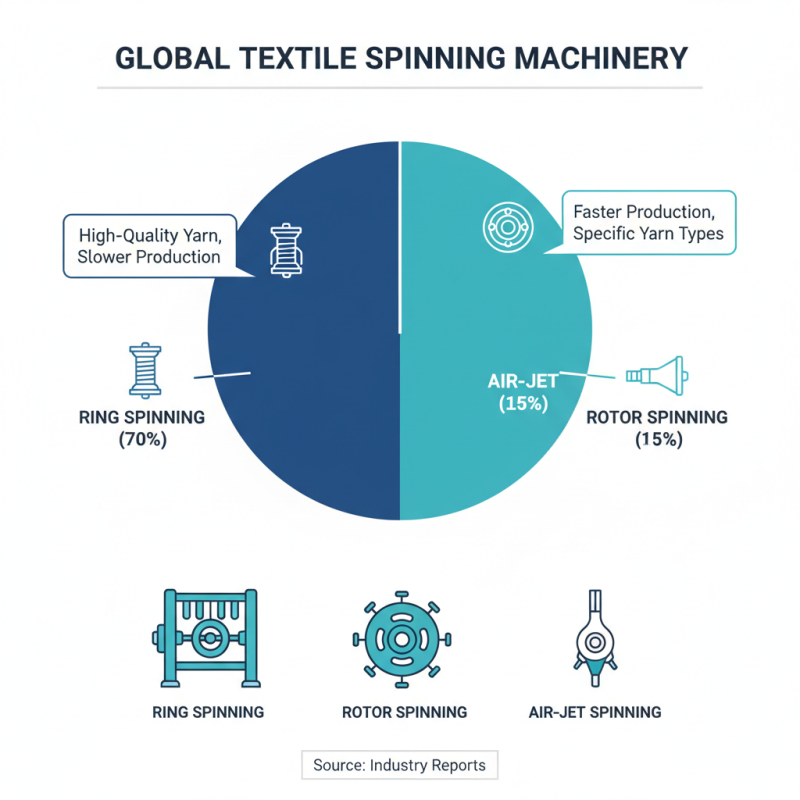
In the textile industry, spinning machinery plays a crucial role. Types like ring spinning, rotor spinning, and air-jet spinning are essential for yarn production. According to industry reports, ring spinning remains dominant, representing 70% of the global market share. It offers high-quality yarns but is slower in production speed compared to other methods.
Rotor spinning, while less popular, has increased in use. It is faster and ideal for producing coarse yarns. Recent data shows that rotor spinning machines can produce 200% more yarn than traditional methods in some scenarios. However, this can sacrifice yarn quality. The choice of spinning method often depends on specific project requirements, making it essential to weigh speed against quality.
Air-jet spinning is gaining traction as a newer technology. It combines efficiency with decent yarn quality. It claims 30% less energy consumption compared to ring spinning. Yet, some users report challenges with consistency. Overall, each spinning type has its strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these intricacies is necessary for optimizing production in the textile sector.
Essential Weaving Machines for Fabric Production
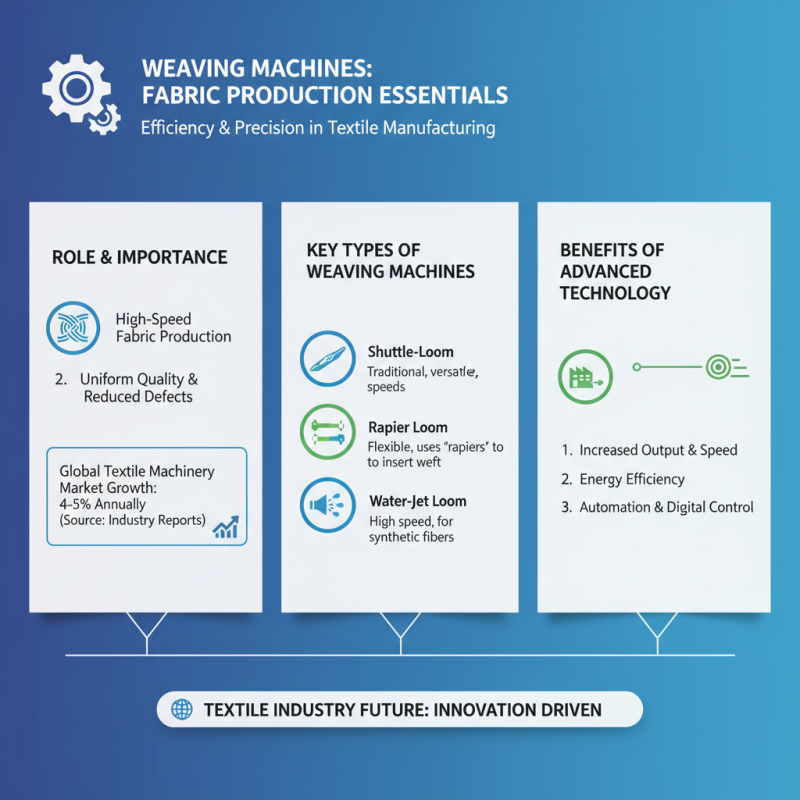
Weaving machines play a critical role in fabric production, providing efficiency and precision. Understanding the various types is essential for anyone in the textile industry. According to recent industry reports, global textile machinery demand is projected to grow by 4-5% annually. This growth reflects the increasing need for advanced weaving technologies.
There are several essential types of weaving machines. The most common are shuttle looms, rapier looms, and air-jet looms. Shuttle looms are traditional and reliable, but they can be slow. Rapier looms, on the other hand, offer higher speeds and flexibility in fabric design. Air-jet looms are known for their high-speed operation and are ideal for mass production. These machines allow manufacturers to improve productivity and reduce costs significantly.
**Tip:** When selecting a loom, consider the fabric type and production volume. Different looms excel in various scenarios. Also, remember that upgrading older machines can lead to efficiency gains, though it may require an initial investment. Machine maintenance is crucial. Neglect can lead to frequent breakdowns, causing delays in production. Evaluate your options carefully; the right choice can transform your production line.
Innovative Knitting Machines: A Closer Look
Knitting machines have evolved into highly innovative tools in textile manufacturing. They offer speed and efficiency, producing complex patterns with precision. Modern machines feature advanced software for design customization, allowing for unique textiles tailored to specific demands. The ability to knit various yarn types enhances versatility. However, these innovations come with a learning curve.
Operators must adapt to new technologies and workflows. While many machines are user-friendly, the complexity of features can be overwhelming. There is always a risk of errors in programming or setup. Misconfigurations can lead to material waste and financial loss. Understanding machine capabilities is crucial for optimal output.
Despite the challenges, innovative knitting machines drive the textile industry forward. Their capabilities push boundaries in design and production. The potential for creating sustainable textiles also prompts reflection on environmental impact. As the industry embraces change, the balance between innovation and mindful manufacturing remains essential. Each advancement should be approached with careful consideration and responsibility.
Top Textile Machinery Types You Need to Know About - Innovative Knitting Machines: A Closer Look
| Machine Type | Key Features | Applications | Production Speed (m/min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Circular Knitting Machine | High efficiency, versatile gauge options, quick changeover | Activewear, socks, and seamless garments | 150-200 |
| Flat Knitting Machine | Computerized control, multi-pattern capability | Sweaters, T-shirts, and high-end fashion | 80-120 |
| Weft Knitting Machine | Robust design, efficient yarn consumption | Home textiles, lingerie, and upholstery | 100-180 |
| Jacquard Knitting Machine | Complex pattern capability, high flexibility | Fashion apparel, functional textiles | 60-100 |
| Warp Knitting Machine | High production rates, improved fabric stability | Sportswear, lingerie, and technical textiles | 200-300 |
Finishing Equipment: Enhancing the Quality of Textiles
Finishing equipment plays a vital role in the textile industry. This equipment is essential for enhancing the quality and feel of fabrics. Various types include
coating machines,
brushing machines, and
calenders. Each type serves a unique purpose, ensuring textiles meet specific standards.
Coating machines apply protective layers to fabrics. They improve durability and resistance to elements.
Brushing machines, on the other hand, create a softer texture. This process enhances the fabric’s overall comfort.
Calenders smooth the surface of textiles, giving a polished look.
Yet, not all finishing methods yield perfect results. Over-application of finishing agents can lead to stiffness. Sometimes, texture becomes less appealing than intended. It's vital to balance quality with functionality. Continuous experimentation is necessary. This industry thrives on innovation. However, reflections on past mistakes can lead to better practices going forward.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Best Finishing Machines for Quality Print Finishing in 2023
-
Top 10 Benefits of Using Automation Machines for Your Business Efficiency
-

Top 10 Process Machinery Trends Transforming Your Industry in 2023
-

How to Choose the Right Vibratory Polishing Machine for Your Needs
-

Why You Should Choose Dalal Vibro Finishing Machine for Superior Surface Finishing
-
What is Home Engineering and How It Transforms Your Living Space
